Following review article has been published and is freely available on-line:
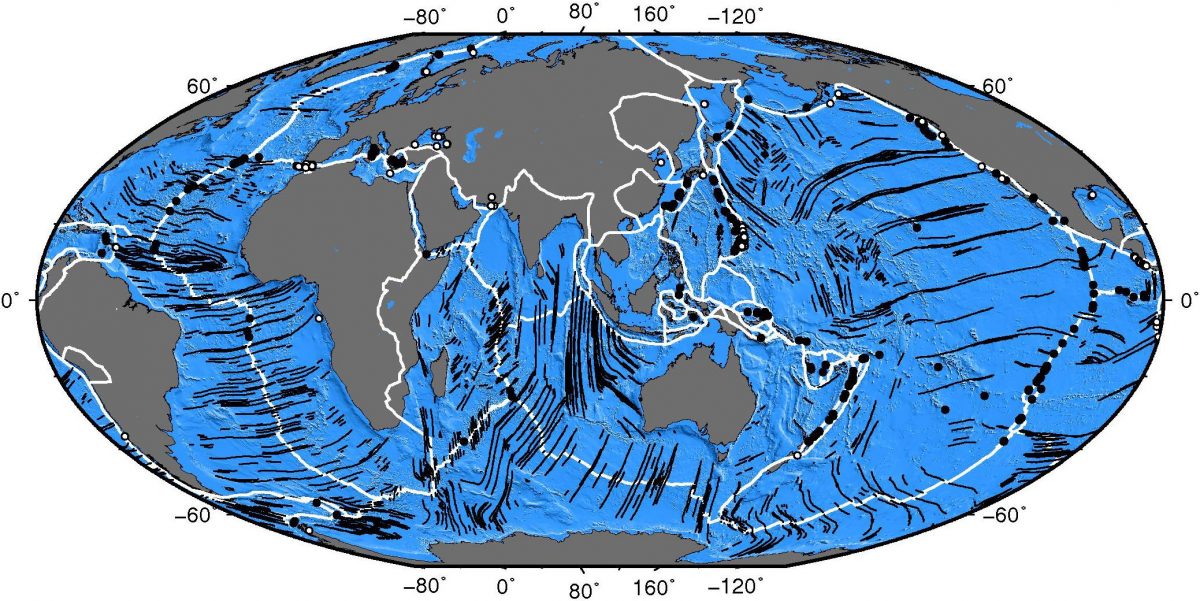
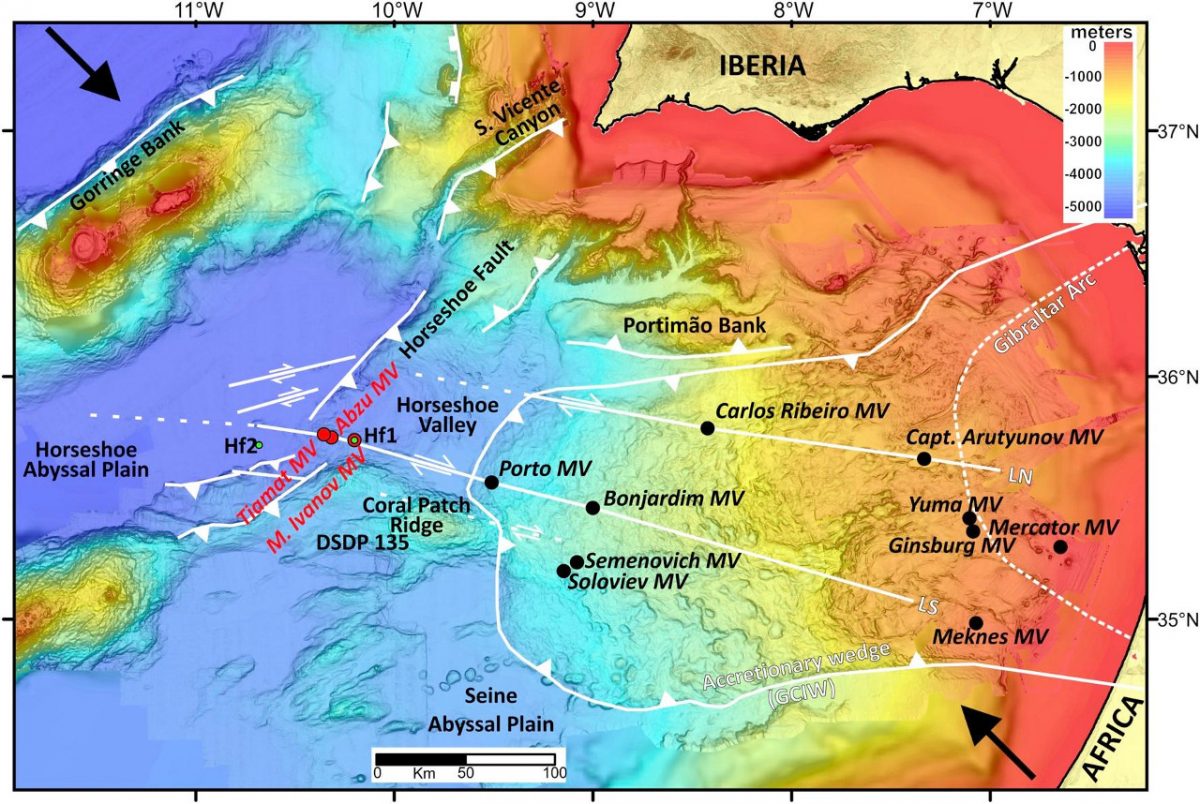
Hensen, C., Duarte, J. C., Vannucchi, P., Mazzini, A., Lever, M. A., Terrinha, P. G., Géli, L., Henry, P., Villinger, H., Morgan, J., Schmidt, M., Gutscher, M.-A., Bartolome, R., Tomonaga, Y., Polonia, A., Gracia, E., Tinivella, U., Lupi, M., Cagatay, M. N., Elvert, M., Sakellariou, D., Matias, L., Kipfer, R., Karageorgis, A. P., Ruffine, L., Liebetrau, V., Pierre, C., Schmidt, C., Batista, L., Gasperini, L., Burwicz, E., Neres, M., & Nuzzo, M. (2019). Marine transform faults and fracture zones: a new perspective integrating seismicity, fluid flow and life, Front. Earth Sci., 7, 39, doi:10.3389/feart.2019.00039.
The manuscript is a joint effort of the scientists involved in the COST Action ES1301 – Impact of Fluid circulation in old oceanic Lithosphere on the seismicity of transfOrm-type plate boundaries: neW solutions for early seismic monitoring of major European Seismogenic zones (FLOWS).